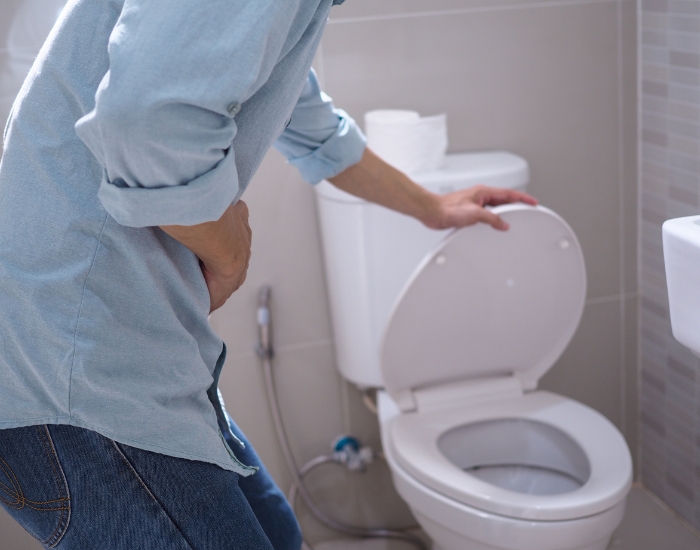
Waking up during the night to urinate can be frustrating and disruptive to your sleep. This condition, medically known as nocturia, affects people of all ages but becomes more common as we get older. While occasional nighttime urination is normal—especially after drinking fluids before bed—frequent trips to the bathroom may signal an underlying health or lifestyle issue. Understanding nighttime urination causes can help you take steps to improve sleep quality and overall well-being.
Table of Contents
- What Is Nighttime Urination?
- Common Nighttime Urination Causes
- When Nighttime Urination Is a Concern
- How Doctors Diagnose the Cause
- Treatment Options for Nighttime Urination
- Can Nighttime Urination Be Prevented?
- Final Thoughts
1. What Is Nighttime Urination (Nocturia)?
Nighttime urination refers to the need to wake from sleep one or more times to pass urine. It becomes clinically significant when it happens regularly and interferes with restful sleep. Some people wake once per night, while others may wake multiple times, leading to daytime fatigue, reduced concentration, and lower quality of life. Nocturia is not a disease itself but a symptom that can result from various conditions affecting the urinary system, sleep patterns, hormones, or overall health.
2. Common Nighttime Urination Causes
Several factors can contribute to frequent urination at night. Often, more than one cause is involved.
Excess Fluid Intake Before Bed
Drinking large amounts of fluids in the evening—especially water, tea, or other beverages—naturally increases urine production overnight. Alcohol and caffeine act as diuretics, stimulating the kidneys to produce more urine and increasing the likelihood of waking to urinate.
Reducing fluid intake two to three hours before bedtime and limiting caffeine or alcohol in the evening can significantly reduce nighttime bathroom trips.
Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder causes sudden, frequent urges to urinate, even when the bladder is not full. These urges can occur during the day or night, leading to disrupted sleep.
Symptoms often include urgency, frequent urination, and occasional leakage. Overactive bladder can result from nerve signals misfiring between the bladder and brain, bladder muscle overactivity, or underlying conditions.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections can irritate the bladder lining, increasing urgency and frequency of urination, including at night. Other symptoms may include burning during urination, cloudy urine, pelvic discomfort, or fever.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are important, as untreated UTIs can worsen or spread to the kidneys.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Imbalances
High blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to remove excess glucose from the bloodstream. This process increases urine production and can lead to frequent urination throughout the day and night.
People with undiagnosed or poorly controlled diabetes may notice excessive thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and nighttime urination as early warning signs.
Sleep Disorders
Certain sleep disorders can contribute to nighttime urination. Obstructive sleep apnea, for example, alters hormone regulation and increases urine production at night. People with sleep apnea may also wake frequently due to breathing interruptions, making them more aware of the need to urinate.
Treating the underlying sleep disorder often improves nocturia symptoms.
Prostate Problems in Men
In men, prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH) is a common cause of nighttime urination. An enlarged prostate can press against the urethra and interfere with normal bladder emptying.
Symptoms may include weak urine stream, difficulty starting urination, frequent urges, and a sensation of incomplete bladder emptying.
Hormonal Changes and Aging
As people age, the body produces less antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which normally reduces urine production at night. Lower ADH levels mean the kidneys produce more urine during sleep hours.
Aging also reduces bladder capacity and the ability to delay urination, making nighttime awakenings more likely.
Heart and Circulatory Conditions
Conditions such as heart failure or chronic venous insufficiency can cause fluid buildup in the legs during the day. When lying down at night, this fluid re-enters the bloodstream and is filtered by the kidneys, increasing nighttime urine output.
Swelling in the ankles or legs during the day may be a clue that fluid redistribution is contributing to nocturia.
Medications
Some medications increase urine production or affect bladder function. Common examples include:
- Diuretics (water pills)
- Blood pressure medications
- Certain antidepressants
Taking diuretics earlier in the day, rather than in the evening, may help reduce nighttime urination. Medication changes should always be discussed with a healthcare provider.
3. When Nighttime Urination Is a Concern
Occasional nighttime urination is usually harmless, but it becomes a concern when it happens frequently or begins to interfere with your sleep and daily functioning. Waking up two or more times each night to urinate, experiencing ongoing sleep disruption, or noticing symptoms that gradually worsen may signal an underlying health issue. Pain or burning during urination, blood in the urine, or nighttime urination accompanied by swelling, shortness of breath, or persistent fatigue should not be ignored. When left unaddressed, ongoing nocturia can increase the risk of falls—especially in older adults—and may negatively affect both physical health and mental well-being due to poor sleep quality.
4. How Doctors Diagnose the Cause
Diagnosing the cause of nighttime urination starts with a thorough review of your medical history and symptoms. Your healthcare provider will typically ask about your daily fluid intake, medication use, sleep patterns, and any related symptoms you may be experiencing. Based on this information, diagnostic tests may be recommended to identify the underlying cause. These can include urine tests to check for infection or elevated glucose levels, blood tests to evaluate kidney function and blood sugar, and bladder diaries to track urination frequency and volume. In some cases, imaging studies or ultrasounds are used to assess structural concerns, while sleep studies may be ordered if sleep apnea is suspected. Pinpointing the exact cause helps ensure a more targeted and effective treatment plan.
5. Treatment Options for Nighttime Urination
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve one or more approaches.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes
- Limit evening fluid intake
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed
- Empty the bladder fully before sleeping
- Elevate legs during the day to reduce fluid buildup
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
Medical Treatments
- Medications for overactive bladder or prostate enlargement
- Antibiotics for urinary tract infections
- Blood sugar management for diabetes
- Adjustments to existing medications
Treating Underlying Conditions
Addressing conditions such as sleep apnea, heart disease, or hormonal imbalances often leads to significant improvement in nocturia symptoms.
6. Can Nighttime Urination Be Prevented?
While not all causes are preventable, many people can reduce nighttime urination with simple changes. Paying attention to hydration timing, managing chronic conditions, and seeking early medical advice can help protect sleep quality and long-term health.
7. Final Thoughts
Nighttime urination causes range from harmless habits to underlying medical conditions that deserve attention. If frequent urination at night is affecting your sleep or daily life, it’s important not to ignore it. Early evaluation can lead to effective treatment, better rest, and improved overall health. If you’re experiencing persistent nocturia, consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and develop a personalized care plan.
If nighttime urination is disrupting your sleep or affecting your daily energy levels, professional medical guidance can help identify the cause and provide relief. The experienced team at Stafford Family Practice offers personalized evaluations and treatment plans to address urinary concerns and underlying health conditions. Scheduling a visit can be the first step toward better sleep and improved overall well-being.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with questions about symptoms or medical conditions. Do not ignore or delay seeking medical care based on information found in this content.